|


 |
Parasitology
Parasitology is the study which primarily concerned in the dependence of one living organism with another while the Medical Parasitology is concern with the parasites that are clinically significant. Many organisms develop their unique relationship with one another. The term symbiosis refer to the two different organism that is living together. Most of the parasites are often described according to their habitat. Sarcoptes scabiei and Pediculus humanus capitis are both example of ectoparasites, these parasites are both usually found outside the host. Some parasites are usually found inside our body and are called endoparasites, for example Ascaris lumbricoides which is found in intestines. Parasites can also be classified according to their mode of living; most parasites are obligate, while some are facultative, temporary, accidental, spurious or even permanent parasites.
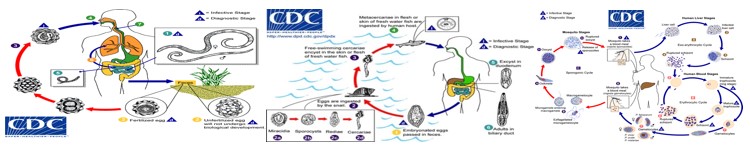
The host is the one who harbor the parasite it can be classified in different types according to their life cycle. The definitive host which is the one who obtain sexual maturity and this is pathologic while the intermediate host is the one who harbors the larval stage and mostly has no pathology. Parasites depend on their host for their food or nourishment, habitat or shelter and for their protection. There are various sources of parasite infections. Contaminated soil and water, lack of sanitary toilets and foods that we eat which contain infective stage of the parasite are the most common sources of infection. Since this are the most common sources of infection possibly the portal of entry is the mouth. Another possible portal of entry is through skin penetration, congenital transmission or inhalation.
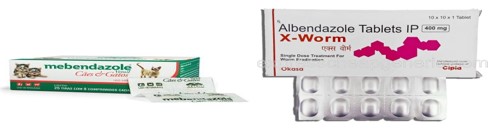
Different treatments for parasitism available depending on the parasite infecting or infesting the host. For parasitic worms, selective treatment involves individual-level deworming, targeted treatment is group-level deworming, and universal treatment is population-level deworming. Drugs such as Mebendazole, Albendazole and Pyrantel Pamoate are also available. Common prevention and control measures are the avoidance of illness, health education, safe disposal of human excreta and personal hygiene.
|
|



