|

 |
Hematology
The history of hematology dates back to ancient Egypt and the use of blood-letting tools. The major breakthrough in the study of blood occurred in 1642 when Anthony van Leeuwenhoek built a microscope and identified blood cells. In 1770, William Hewson, the 'Father of Hematology', introduced the clotting features of blood and shared his knowledge of leukocytes, or white blood cells (Danielle Haak, 2013).
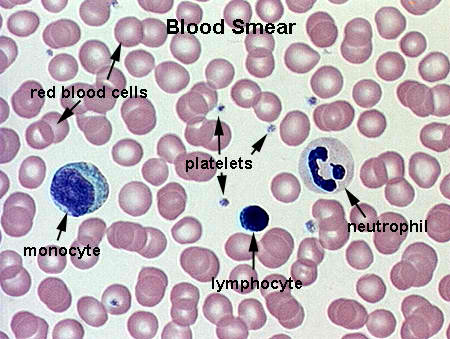
The scientist or doctors who specialized in the care and treatment of hematological diseases are known as Hematologists. The study of hematology is concerned in the health and diseases of blood. It includes abnormalities with the red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, blood vessels, spleen and the proteins involved in the blooding and clotting.
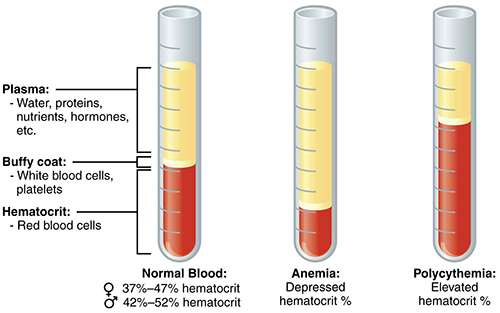
One of the most common disorder of blood is Anemia. Anemia happens when there is no enough supply of red blood cells or when the red blood cells is not functioning properly. When a person has anemia, he/she lacks of oxygen and can experience weakness, shortness of breath, pounding, pale or yellow skin and chest pain.
There are common types of anemia, includes, Iron deficiency anemia which is the most common type of anemia. Aplastic anemia, occurs when the body stops making red blood cells due to a viral infection and toxic chemicals. Hemolytic anemia happens when the red bloods cells is damage in the bloodstream or spleen. Sickle cell anemia is caused by an abnormal hemoglobin protein, causing the red blood cell to block in the circulation.
Anemia can be treated but it depends on what causes it. For example, Aplastic anemia may be due to primary bone marrow failure or occasionally as a side effect of some medications, if you appear to have an aplastic anemia, the doctor may refer to a hematologist for a bone marrow biopsy to determine the cause of the anemia. Medications and blood transfusions may be used to treat aplastic anemia (American Society of Hematology, 2016).
Some type of anemia can be prevented but many of them cannot be prevented. However, Iron deficiency anemia can be prevented by dietary changes or by choosing a diet that includes variety of vitamins and food that is rich in iron, including pork, sea foods, beans, dried fruit and dark green leafy vegetable, such as spinach.
|
|



